Aluminum Alloy Die-Casting Mold Maintenance and Care: Ensuring Production Efficiency and Product Quality
Table of Contents
The maintenance and care of aluminum alloy die-casting molds are crucial for ensuring production efficiency, improving product quality, and reducing production costs. The lifespan of the mold directly impacts production costs and product quality. Therefore, proper mold management can not only improve production efficiency but also reduce potential maintenance costs and unnecessary downtime.
1. Why Mold Maintenance is Crucial
During the die-casting production process, the condition of the mold directly affects product quality and production continuity. Regular and effective mold maintenance can extend the mold’s lifespan, reduce repair times, and minimize the risk of malfunctions during production.
2. Establishing a Mold File: Optimizing Management and Maintenance
1. Create Detailed Record Systems
Every mold entering the production line should have a comprehensive usage record. This record should include detailed information about each production cycle, such as wear, frequency of use, and any issues that arise. These documents serve as essential references for future maintenance and upkeep.
2. Categorize Mold Components for Readiness
To ensure the timely replacement and repair of mold components, detailed records of each mold’s parts should be maintained. Regular checks of commonly worn parts (such as ejector pins and cores) are vital. Maintaining a minimum inventory level for these parts is crucial to avoid production delays and reduce costs.
3. Apply Permanent Mold Markings
Permanent markings on molds help prevent incorrect installations and ensure proper mold usage. These markings allow operators to quickly verify the mold’s status and usage history, preventing unnecessary wear.

4. Use Quick Connect Fittings
Using quick connect fittings can significantly reduce mold installation and teardown times, enhancing production efficiency. Molds with hydraulic core pullers can benefit from these fittings, reducing waste and increasing operational flexibility.
5. Standardize Mold Management
Establishing detailed operational procedures for mold management and training operators ensures that maintenance procedures are executed consistently. Standardized execution of mold care will improve production efficiency and product consistency.
3. Key Considerations During Mold Operation
Operators play a vital role in mold maintenance. Their practices during mold use can have lasting effects on the mold’s condition.
1. Effective Use of Mold Cooling Systems
Proper management of mold cooling systems extends mold life and improves productivity. Ignoring cooling systems can lead to cracks and deformations in the mold, which will affect product quality and production cycles.
2. Preheating Molds Before Use
Preheating molds prevents thermal shock caused by hot metal, reducing the risk of cracks and prolonging the mold’s operational life. Techniques like gas torches or dedicated mold heaters can ensure gradual temperature transitions.
3. Regularly Clean Mold Parting Lines
Parting lines are susceptible to buildup of aluminum residue or carbon deposits. Cleaning these areas regularly not only extends the mold’s life but also ensures that cast parts maintain their quality and reduces the likelihood of leakage.
4. Maintain Signal Line Integrity
Ensuring uninterrupted signal lines between die-casting machines and molds prevents equipment malfunctions and potential mold damage.
5. Regular Inspection and Maintenance
Operators should follow established inspection checklists to perform detailed assessments, identifying and resolving potential issues to maintain production continuity and efficiency.
4. Preventive Care and Maintenance
1. Post-Production Mold Inspections
Mold technicians should thoroughly inspect molds after each production run, noting any incidents or repairs and updating mold files with the latest production cycle data.
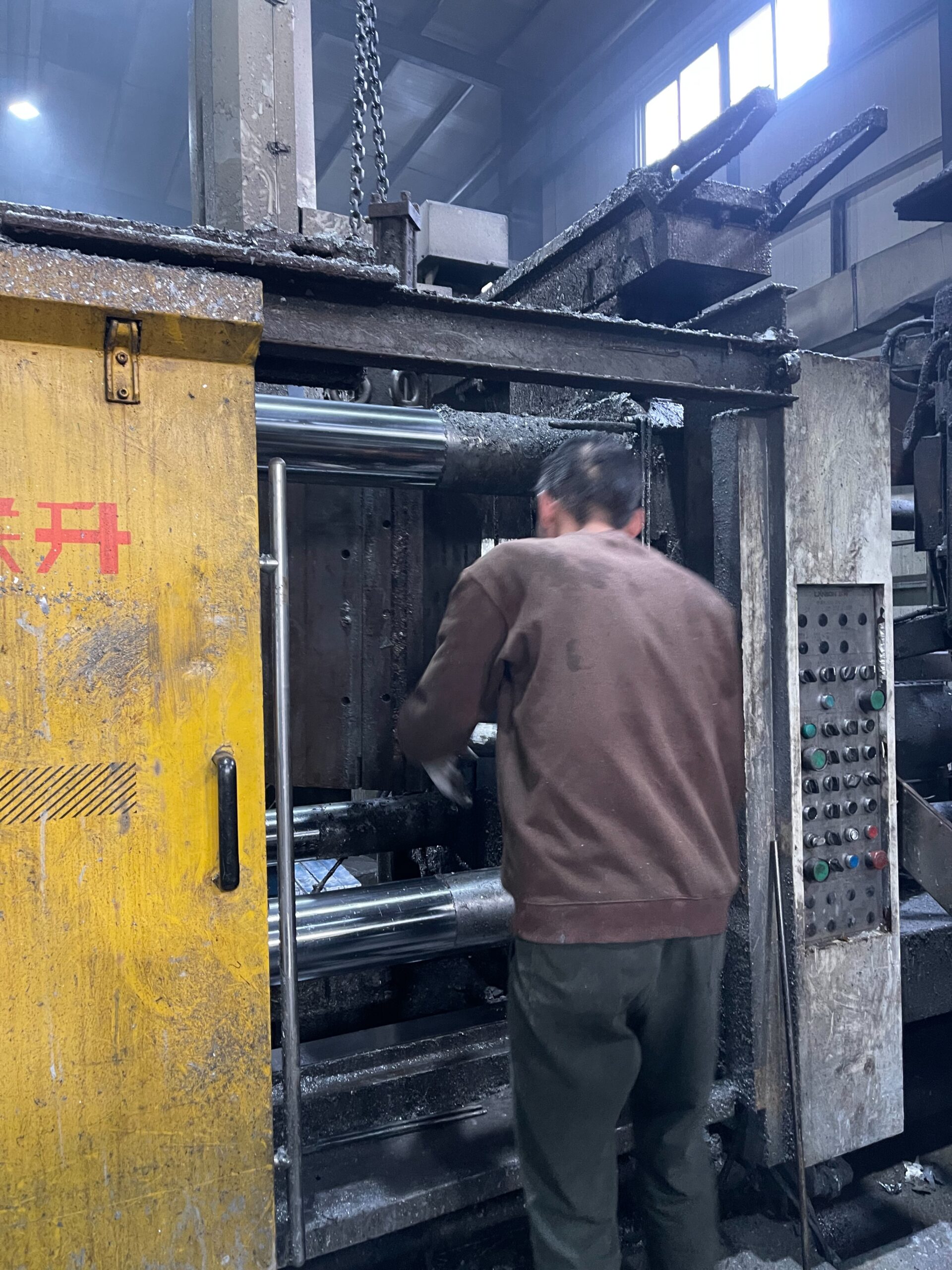

2. Strict Adherence to Maintenance Protocols
To maintain mold integrity, unauthorized dimensional changes should be avoided, and strict adherence to maintenance guidelines must be ensured. This helps reduce the risk of mold deformation or damage that could lead to production downtime.
3. Address Wear and Damage to Moving Parts
Moving components like ejector pins experience significant stress and should be regularly checked for wear or cracks. Timely replacement is essential to avoid failures during future production cycles.
4. Polishing and Surface Care
Targeted polishing focuses on areas with aluminum residue or carbon deposits to reduce unnecessary abrasion, ensuring a smooth mold surface for better precision and finish.
5. Lubrication and Rust Prevention
Lubrication and rust prevention are essential for maintaining the functionality and longevity of moving parts and connections. Regular treatment, especially for molds not in use for extended periods, will prevent rust and ensure proper operation.
6. Preservation of Mold Storage Records
Keep consistent records across mold logbooks, drawings, and archival documentation. Regular rust-prevention treatments for molds that are unused for long periods can help extend their lifespan.
5. Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How can improper mold maintenance affect production costs?
Improper mold maintenance leads to frequent breakdowns, which increases repair costs, reduces production efficiency, and raises defect rates, all contributing to higher production costs.
Q2: Why is it important to preheat molds before use?
Preheating molds prevents thermal shock from the hot metal, reducing the risk of cracks and prolonging the mold’s operational life.
Q3: What is the role of a mold file?
A mold file is essential for tracking a mold’s operational history, aiding in scheduling maintenance, managing parts inventory, and preventing future issues.



